We often see leftovers as a convenient next-day meal, but lurking within could be unseen risks. The tragic tale of a 20-year-old Belgian man’s death from “fried rice syndrome” after eating leftover spaghetti serves as a stark warning.
Despite the innocuous nature of saving food for later, this incident reveals how simple habits can turn deadly. Bacillus cereus, the culprit behind this syndrome, thrives in improperly stored food, turning a meal into a fatal mistake.
What is ‘Fried Rice Syndrome’?

“Fried rice syndrome” may sound trivial, but it’s a serious food-borne illness caused by the bacteria Bacillus cereus. This bacteria rapidly grows when food is left out at room temperature and can survive extremely high cooking temperatures.
Ingesting food contaminated with Bacillus cereus can lead to severe food poisoning and, in some cases, death.
The Danger of Room Temperature

While Bacillus cereus is most commonly found in pasta, rice, and other starches or grains, it can also present in meat, vegetables, and even herbs and spices.
Essentially, the toxic bacteria can grow in almost any food that has been left out at room temperature after being cooked.
Common Misconceptions about Reheating Food

Many believe that freezing leftover or reheating food kills absolutely any bacteria; however, that is not always the case.
What’s especially dangerous about Bacillus cereus is that it can continue to live in leftovers even after they have been moved to the fridge or freezer or even reheated.
Understanding Bacillus Cereus
According to the BC Center for Disease Control, Bacillus cereus is notorious for causing two types of food poisoning: emetic and diarrheal.
Emetic or vomiting syndrome can cause vomiting and intense nausea, while diarrheal syndrome causes diarrhea, often with blood or mucus, and severe abdominal pain.
The Symptoms of “Fried Rice Syndrome” Are Not Always Severe

It’s important to note that while the symptoms can be incredibly painful, not all those who ingest Bacillus cereus will experience severe symptoms.
For some, it could simply feel like a mild case of food poisoning. But others, depending on their body and the amount of bacteria growth in the food, could become dangerously sick and even die from the toxins.
A Tragic Meal

A young man’s life was cut short in Belgium after eating leftover spaghetti. Sadly, about 10 hours after consuming the contaminated meal, he was found deceased.
The 20-year-old had apparently experienced severe headaches, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting in the mere hours between his last meal and his untimely passing. (via Yahoo! News).
The Autopsy Findings

The autopsy of the young man revealed several alarming findings: a moderately softened liver, complete dissolution of the pancreas, and the absence of specific cardiac symptoms.
These findings, particularly the significant liver changes and the absence of mitochondrial damage in cardiac cells, pointed to an indirect cause of death, likely related to systemic reactions like acidosis.
Policed Tested the Leftover Pasta

Meanwhile, the police investigated the young man’s apartment and found remnants of the leftover pasta. In the lab, they noted significant levels of Bacillus cereus and a high concentration of the toxin cereulide.
This finding, along with the pathologist’s report, dictated that the man had indeed died of Bacillus cereus poisoning, or “fried rice syndrome.”
Historical Cases of Bacillus Cereus Outbreaks

Of course, the young man in Belgium is not alone. Every year, millions of people worldwide suffer from foodborne illnesses, with thousands of cases being fatal, and thousands of these cases are the result of Bacillus cereus poisoning.
In fact, a paper from the National Library of Medicine reported that over 7,385 people fell ill from Bacillus cereus bacteria in the United States alone between 1998 and 2015, three of whom died due to the toxin.
How Does Someone Die From “Fried Rice Syndrome”
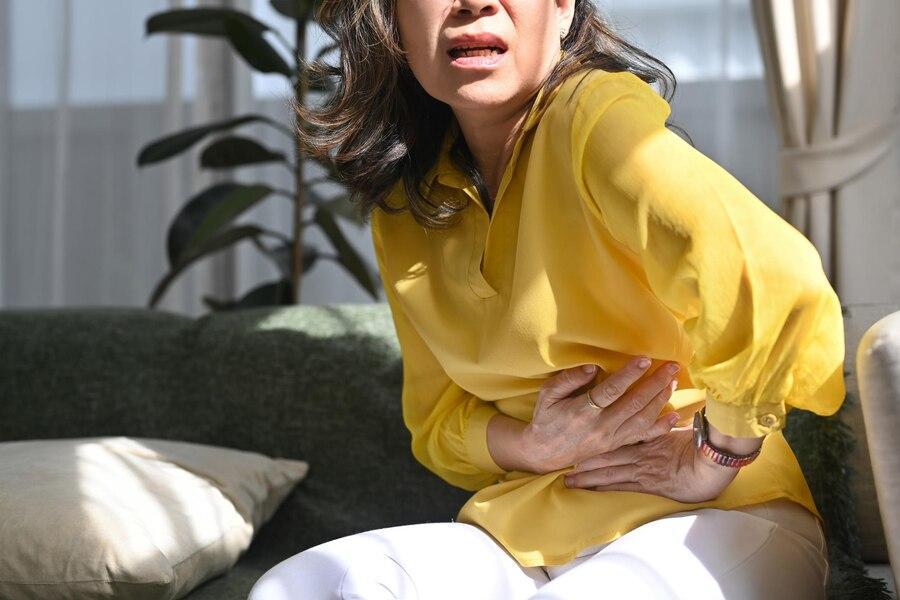

Although “fried rice syndrome” or Bacillus cereus bacteria can be contracted by anyone who eats contaminated food, it is most commonly detrimental to the elderly or those living with a weakened immune system.
The majority of people who die from “fried rice syndrome” experience fatal gastrointestinal syndromes, respiratory tract infections, or organ decomposition, such as the liver or kidneys.
Most People Infected With Bacillus Cereus Fully Recover
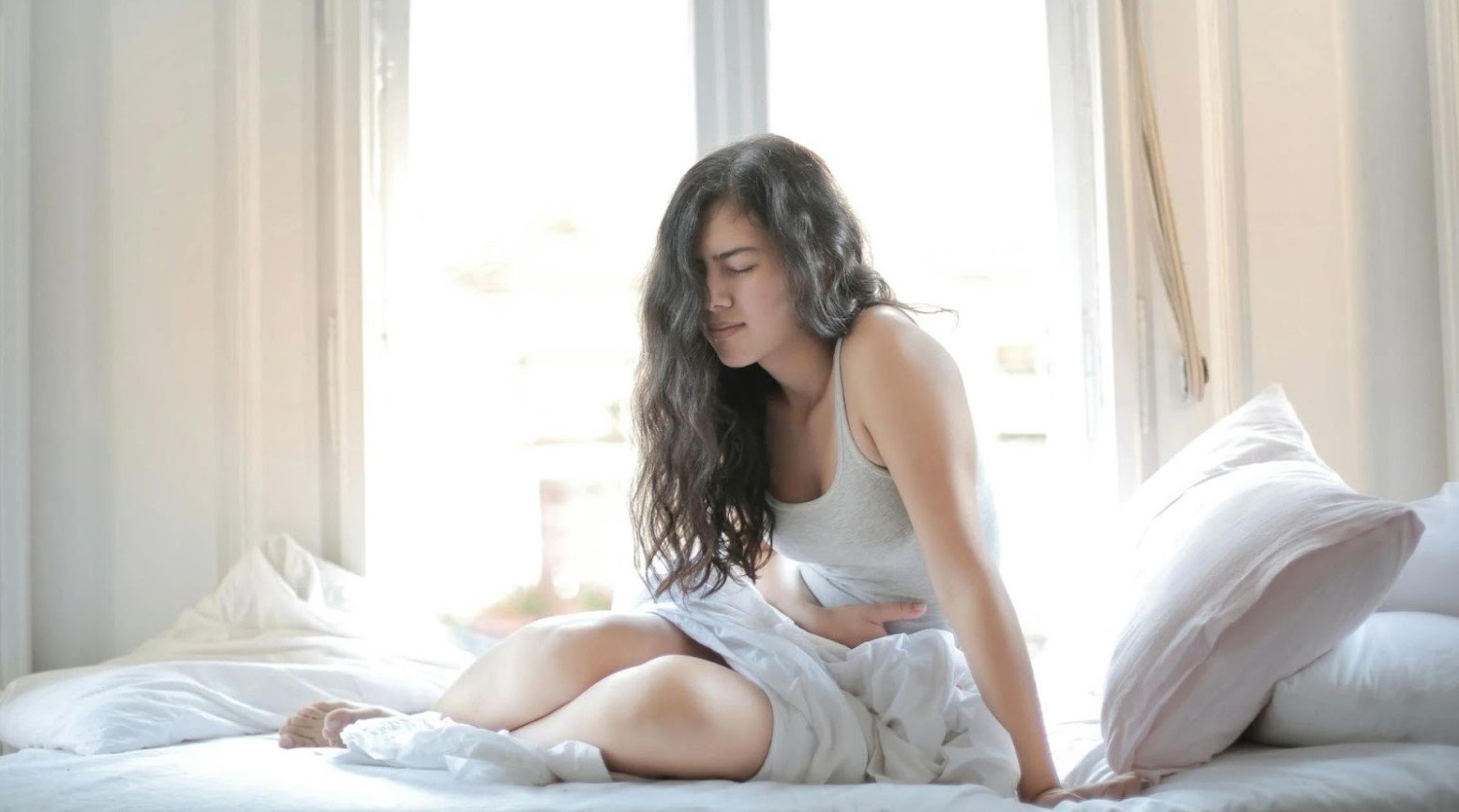

That being said, death is a fairly uncommon result of this food-borne bacterial infection. The vast majority of people who ingest the bacteria fully recover from any subsequent symptoms.
But doctors hope that with the proper education, they can all but stop Bacillus cereus from causing any more damage.
How to Protect Your Food from Bacillus Cereus

However, this story should absolutely serve as a cautionary tale for people all around the world: Food storage safety is extremely important and should be understood by anyone who prepares food for themselves or others.
There are several aspects of food storage and food poisoning that everyone should know, including how to safely store cooked food, how long food can stay at room temperature, exactly how to safely reheat leftovers, and the various symptoms to look out for.
The Importance of Time
Time is of the essence when it comes to food storage. Bacillus cereus can multiply quickly at room temperature, producing toxins that are not destroyed by reheating (via UW Medicine).
Understanding this can help prevent the inclination to leave food out for convenience, safeguarding against potential illness.
How Long Can Food Stay at Room Temperature?
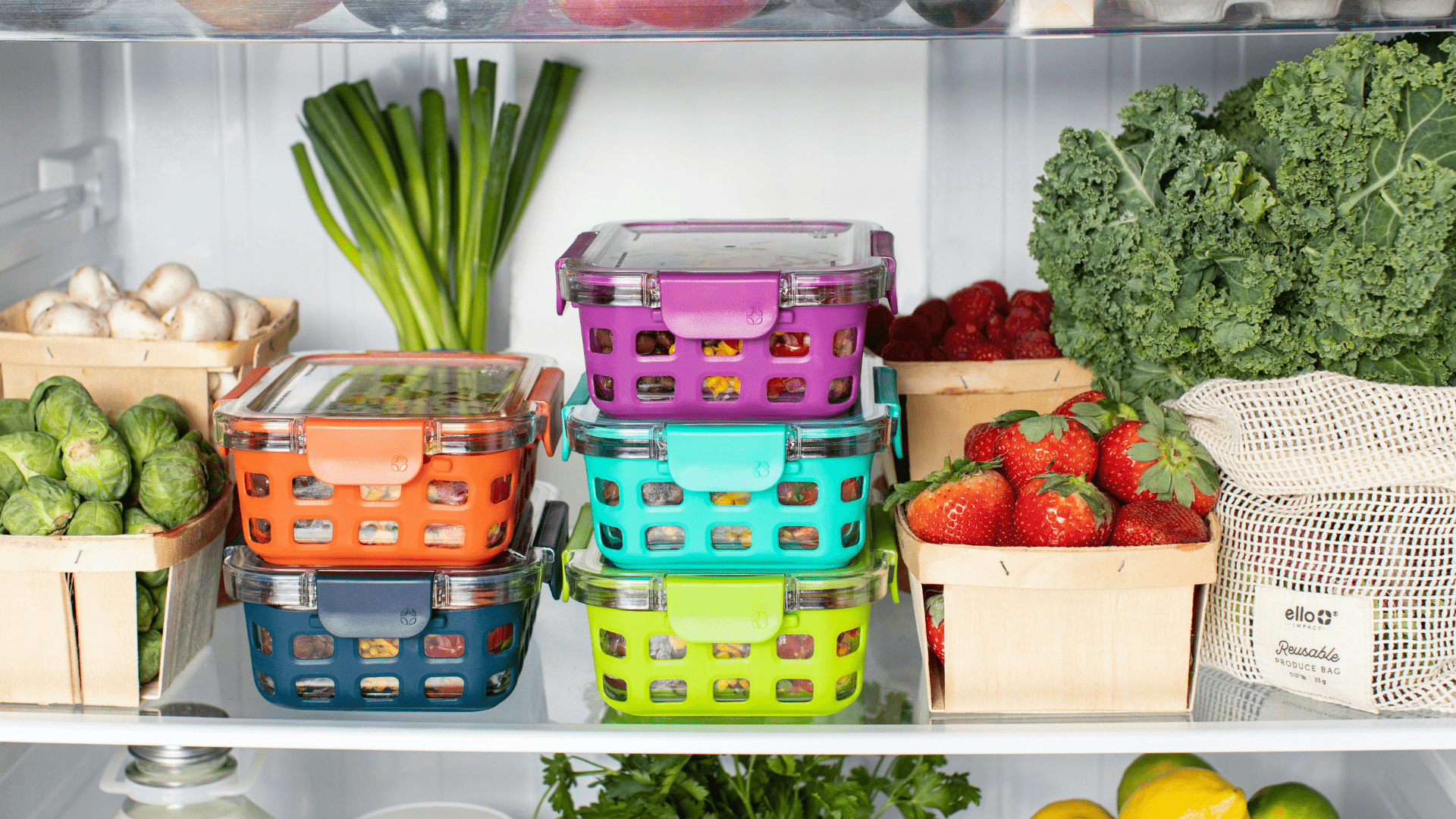

To avoid the growth of Bacillus cereus, it’s crucial to cool and refrigerate leftovers promptly. Cooked food should never be left at room temperature for extended periods.
However, it is unsafe to transfer hot or even warm food into the refrigerator before it has reached room temperature. The general recommendation is that food should be left to cool to room temperature, but it should never be left out for more than two hours.
Tips for Quick Cooling of Leftovers

To speed up the cooling process for leftovers, divide them into smaller portions or use shallow containers.
This method allows the food to cool more quickly and evenly, reducing the time it spends in the temperature danger zone before being safely moved to the refrigerator.
Proper Storage Temperatures
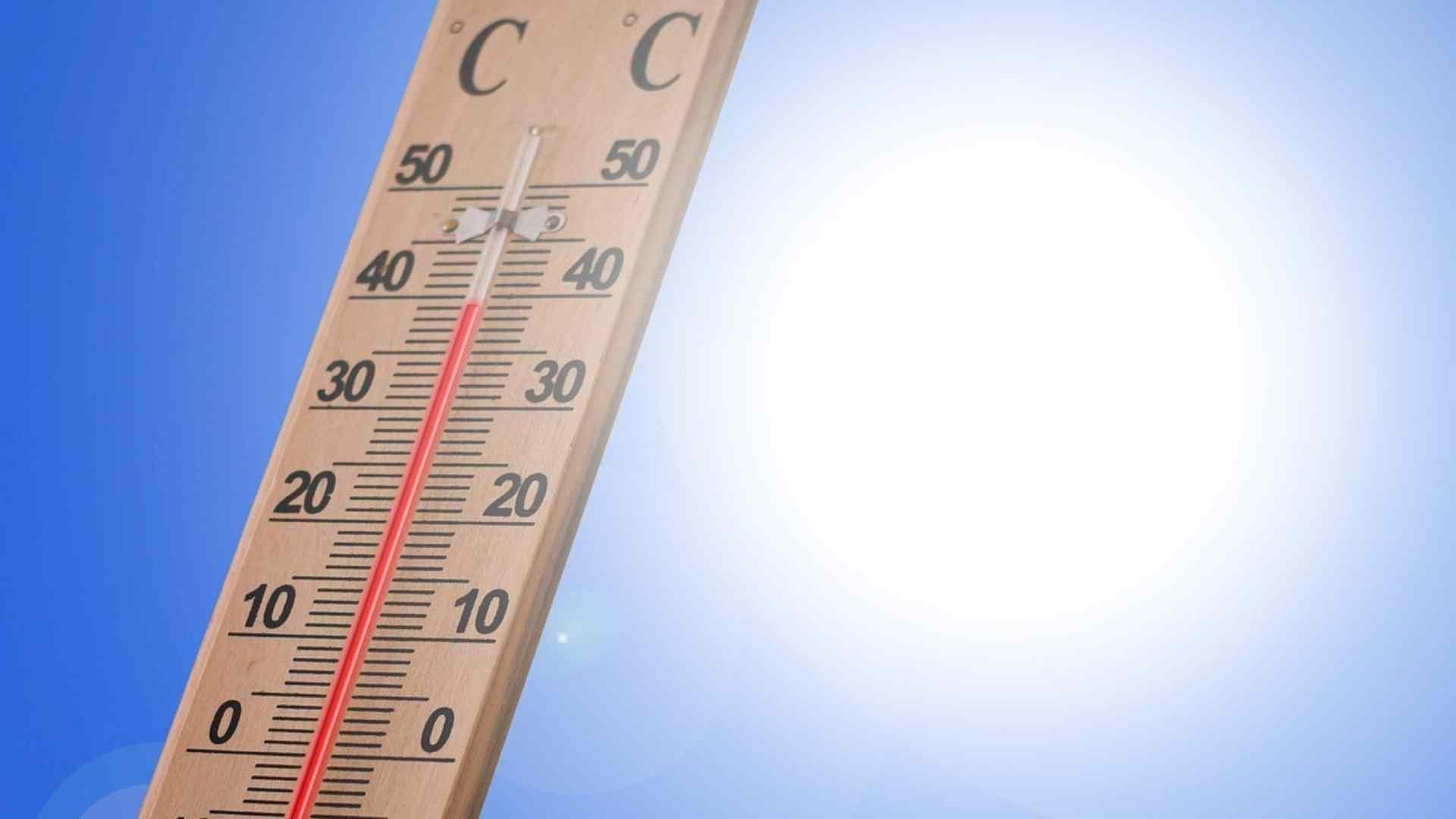

Food should be stored at safe temperatures to prevent bacterial growth. Per the FDA guidelines, the safe refrigerator temperature is at or below 40°F, and the freezer temperature should be 0°F.
Sticking to these temperatures can drastically reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses in any and all kinds of food.
The Role of Oxygen in Bacterial Growth

Many bacteria, including Bacillus cereus, need oxygen to grow (via Purdue University).
Therefore, using airtight containers when storing food can limit the amount of oxygen available, inhibiting some bacterial growth. This simple practice can be a crucial step in food safety.
How to Safely Store Cooked Food
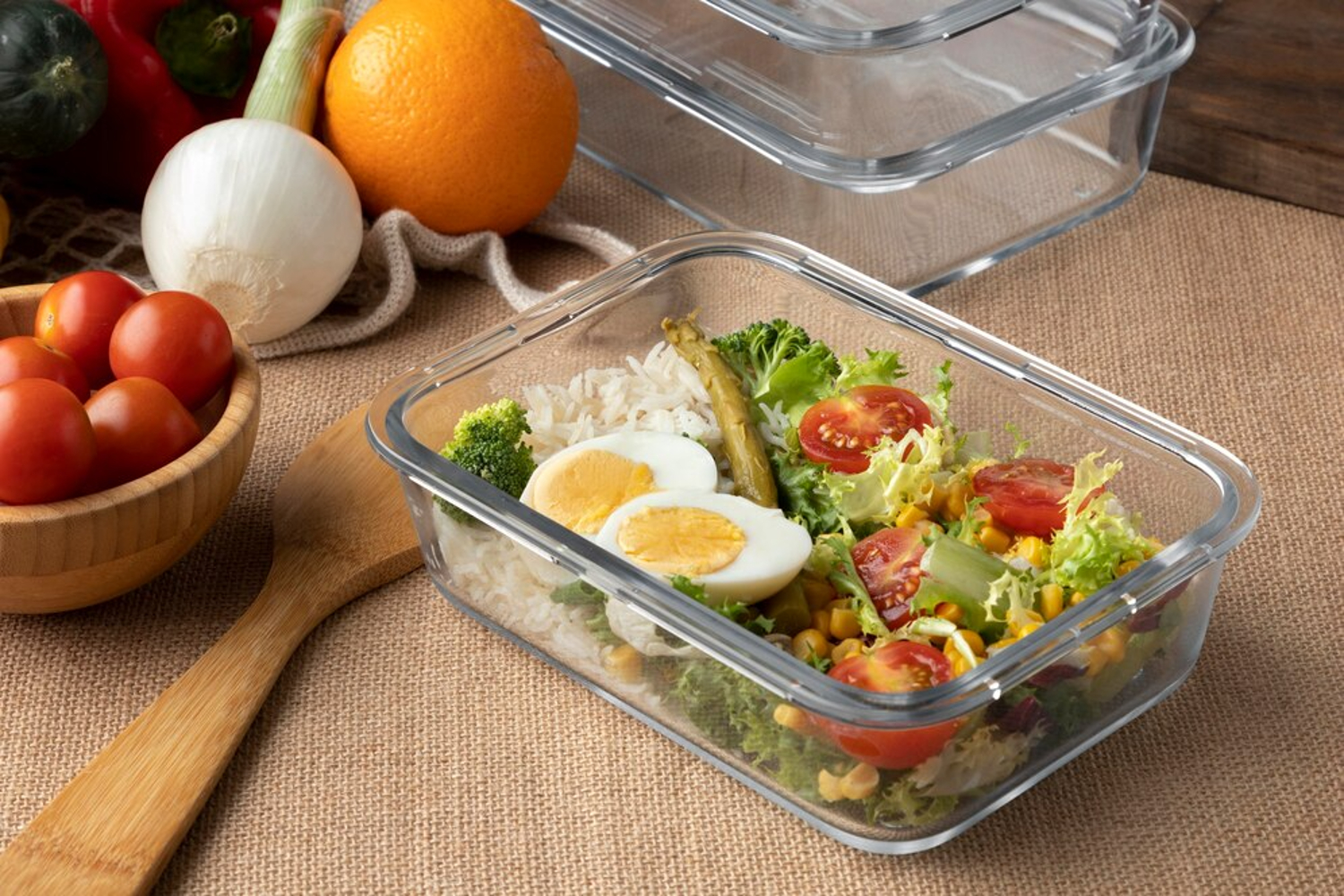

In addition to ensuring that leftover food is in an airtight Tupperware container, hasn’t been left out at room temperature for more than two hours, and is stored at the recommended temperature in the fridge or freezer, it’s also important to ensure the food is not contaminated in the fridge.
Many people are unaware that leaving moldy food in the fridge can actually contaminate other foods, even if they are not directly touching. It is crucial to remove any out-of-date or possibly contaminated food from storage immediately.
How to Safely Reheat Leftovers

Along with knowing how to properly store food, it’s equally important to learn how to safely reheat leftovers to ensure that any residual bacteria are completely obliterated.
Although reheating can never 100% guarantee that all bacteria will be eliminated, the majority of food-borne bacteria and viruses will be killed when food is heated properly.
How Hot Should Food Be When Reheated?
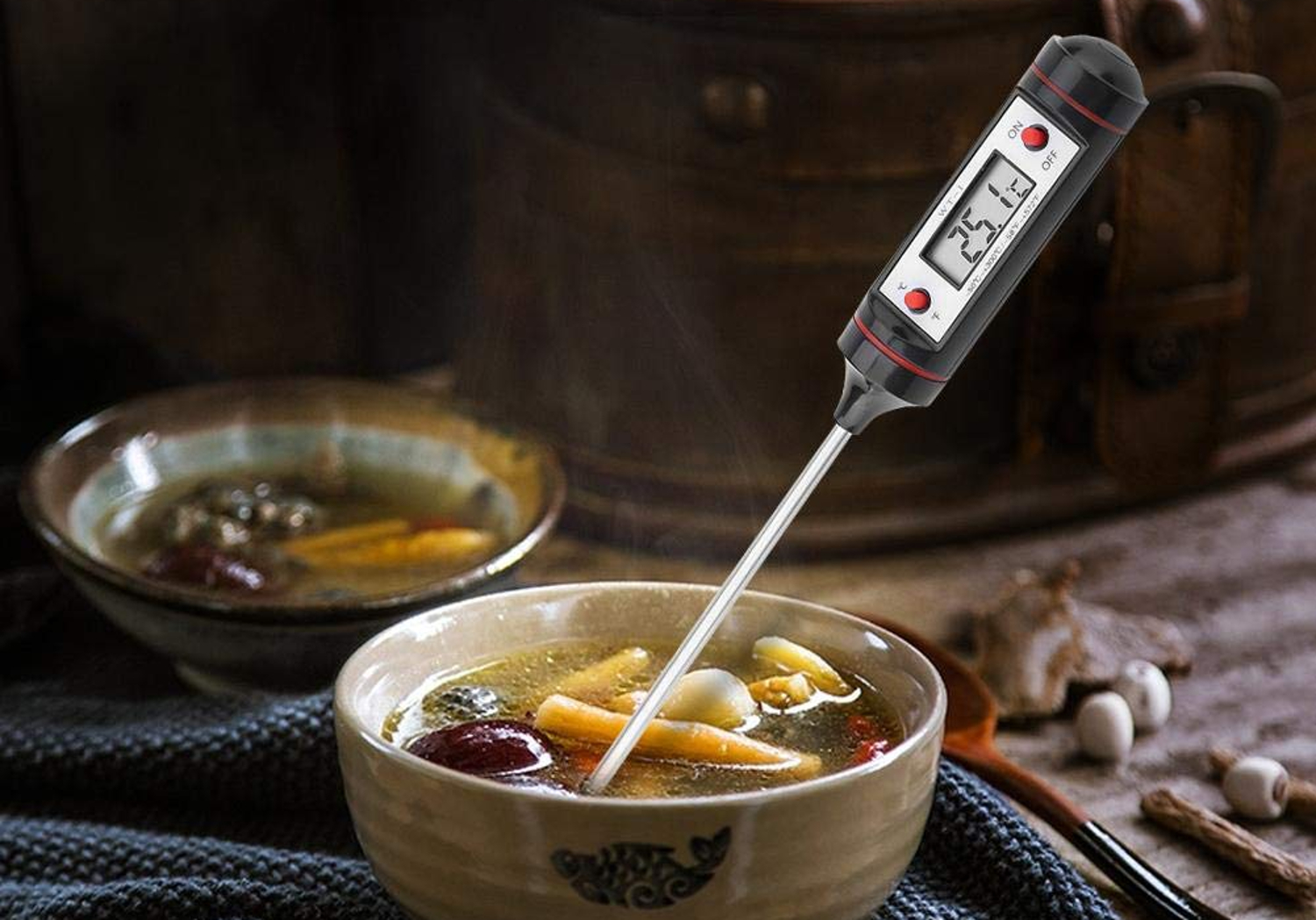

According to the USDA, all food should reach at least 165 °F when reheated before it is consumed.
Of course, it’s impossible to know a food’s internal temperature just by looking at it, and every reheat is a little different. Therefore, the USDA recommends using a food thermometer when reheating any kind of food, especially those that are known to cause food poisoning.
Is it Safe to Reheat Food in a Microwave?
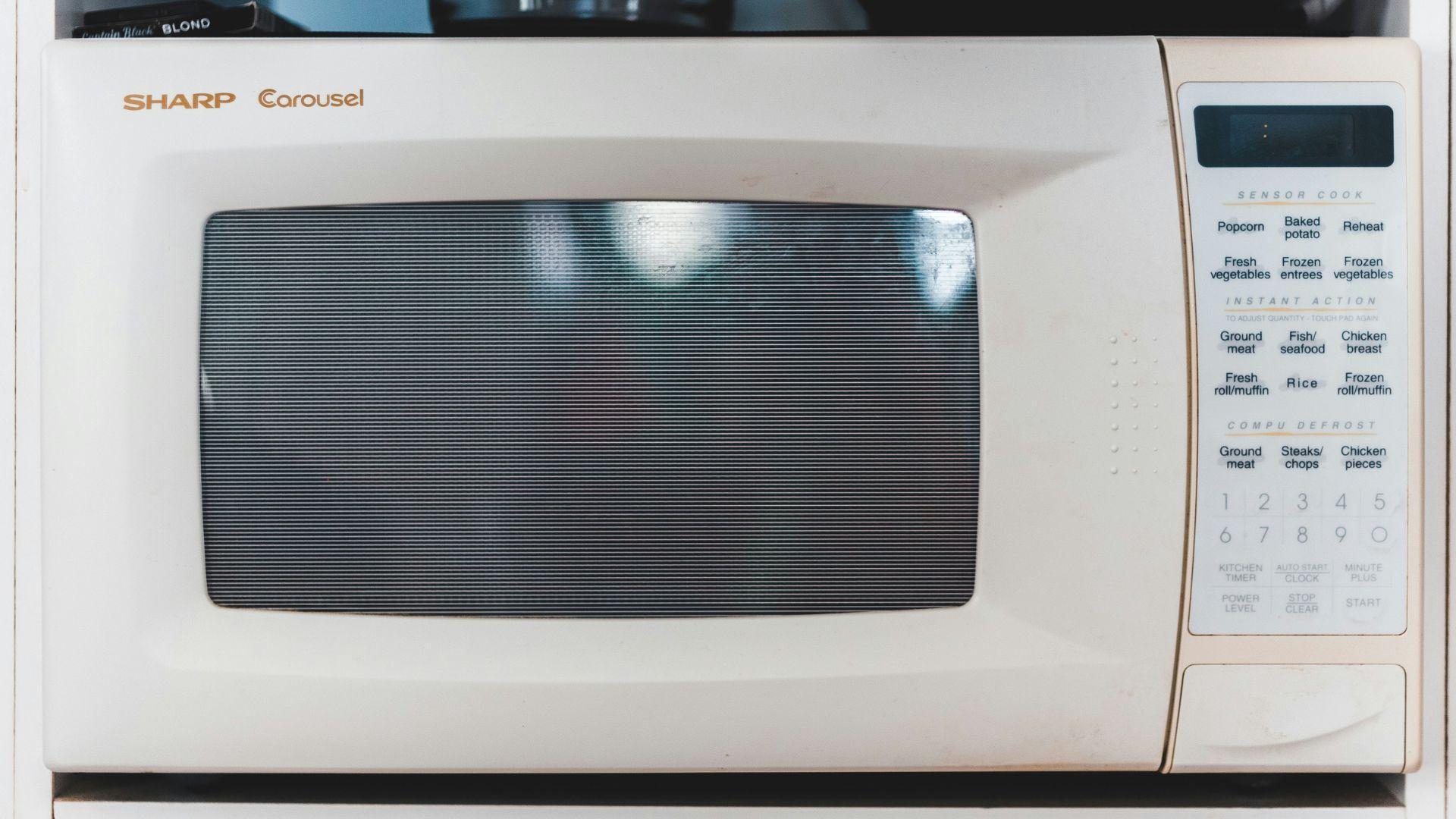

When it comes to food safety and reheating, one of the most commonly asked questions is whether it’s okay to reheat leftovers in a microwave.
According to the BBC, microwaves are not the best way to reheat food as they heat from the outside in, leaving cool pockets where bacteria can thrive. If you do choose to reheat in the microwave, it’s vital that you take the food out, stir it, and then reheat it at least once more before consumption.
What Is the Best Way to Reheat Food?
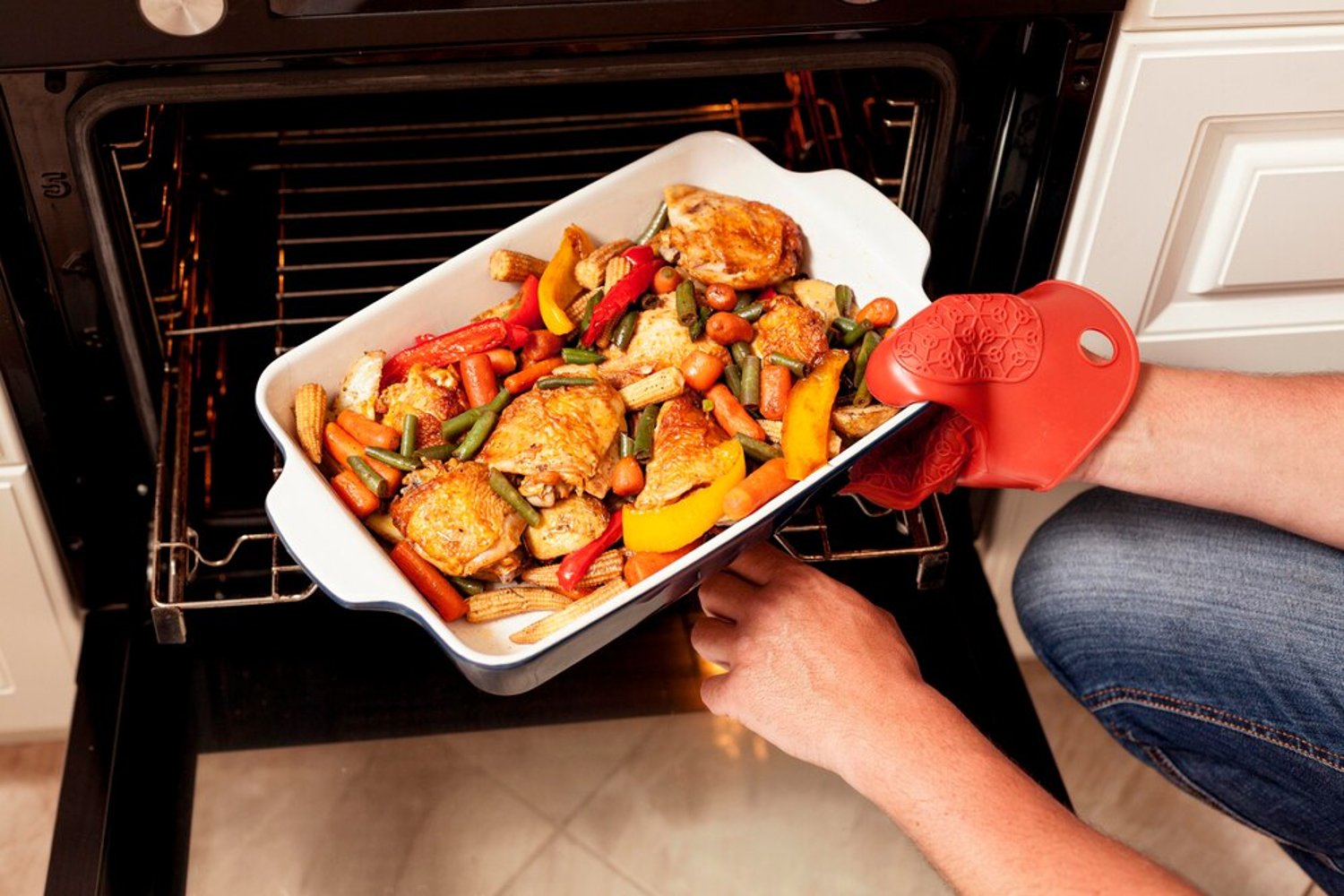

Realistically, the microwave is not the best or safest way to reheat leftover food. The USDA explained that microwaves, steam tables, slow cookers, and chafing dishes are all potentially dangerous options.
Instead, the organization explains, using a stove or oven to reheat food are the two best, and really the only safe, options.
How Many Times Can Food Be Reheated?

Another commonly asked question is how many times food can safely be reheated. In theory, food can be reheated multiple times as long as its done so correctly, but that’s not the official recommendation.
The Food Standards Agency reports that leftover food should only be reheated once. Unfortunately, once it gets cold again, it is no longer completely safe to eat.
Some Bacteria Are Particularly Heat Resistant

While these tactics are certainly important to know and practice, everyone should also understand that certain bacteria are heat resistant.
Bacillus cereus is one of those heat-resistant bacteria, which is why “fried rice syndrome” is so dangerous.
“Friend Rice Syndrome” Can Be Fatal

The swift onset of severe symptoms leading to the young man’s death within hours of eating contaminated food illustrates the potent danger of food poisoning.
While many cases of food poisoning are mild, Bacillus cereus can have devastating, even fatal, consequences. Therefore, it’s crucial to learn about the various symptoms one might encounter and when to contact a medical professional.
The Symptoms of Food Poisoning

The CDC reports that the most common symptoms of food poisoning are cramps, stomach pains, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever.
However, depending on the type of bacteria and the body it has entered, these symptoms can vary in how and when they present, as well as the severity. So it’s extremely important that you know your own body and can determine what feels abnormal.
When Do Symptoms of Food Poisoning Set In?

For most people, the symptoms of food poisoning will set in between 30 minutes and 12 hours after they consume contaminated food.
That being said, some people don’t see any symptoms for until almost three days later. It all depends on the digestive system, the food itself, and the type of bacteria present.
Seeking Medical Attention

The symptoms of food poisoning are often mild or even nonexistent. If the symptoms are light or only last for a few hours, then most people do not need to visit their doctor.
However, if you experience symptoms of food poisoning, such as vomiting or diarrhea, for more than 24 hours, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly.
Monitoring Symptoms and When to Act

It’s important to monitor the severity and duration of food poisoning symptoms. Early intervention can mitigate the effects of the toxins and prevent more severe outcomes.
If symptoms persist or worsen over 24 hours, immediate medical attention is necessary. A quick response can prevent severe dehydration and other potential complications from an otherwise completely curable problem.
What Is the Treatment for Food Poisoning?

If the symptoms are so bad that you need to visit the doctor or even the hospital, the treatment is usually quite simple.
Typically, medical professionals will prescribe IV fluids to replace the electrolytes lost due to dehydration. Though in some cases, they may offer pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, to kill the internal bacteria as quickly as possible.
Why Do People Die From Food Poisoning?

The most common cause of death from food poisoning is severe dehydration. Because the body has been unable to retain water and its minerals after excessive diarrhea or vomiting, it simply shuts down.
But there can be other complications, especially in children, the elderly, or those with a weak immune system, such as infections, kidney failure, liver failure, or heart failure.
How Many People Die From Food Poisoning Every Year?

Sadly, more than 3,000 people die every year from complications from food poisoning in the US alone.
And according to the World Health Organization (WHO), food poisoning causes more than 420,000 annually around the world; 30% of these fatalities occur in children under the age of five.
The Future of Food Safety Technology

While learning about food safety procedures will always be important, advancements in technology, such as smart packaging that detects bacterial growth and apps that track storage times and temperatures, could revolutionize food safety.
Embracing these technologies could greatly reduce the incidence of foodborne illnesses in the future.
The Impact of Foodborne Illnesses on Public Health

Many people don’t realize that food-borne illnesses not only affect individual health but also impose significant economic burdens on healthcare systems and businesses.
According to ScienceDirect, food-borne illnesses cost individual states more than $55 billion per year, so ensuring food safety is not just a personal responsibility but a public health priority.
A Call for Awareness

While the incident in Belgium adds to a small but concerning list of fatalities linked to cereulide, it emphasizes the need for heightened awareness and safety practices in food handling and storage.
This tragic case serves as a sobering reminder of the importance of proper food storage practices. As we remember the young man whose life was cut short, it’s important to commit to being more vigilant about how we store and handle our food.








































