The United States presents a complex landscape when it comes to life expectancy. While the average American is living approximately 30 years longer than a century ago, not every state enjoys this longevity equally. The disparities between different regions, particularly between the South and the more affluent Northeast and West Coast, are stark and interesting.
From health care accessibility to lifestyle choices, numerous factors contribute to this imbalance. Here, we uncover why some U.S. states might be shortening your life span and what underlying issues need addressing.
The Southern Health Gap

Southern charm comes with a downside: lower life expectancy. States like Alabama and Mississippi face critical challenges, including limited health care access and higher smoking rates. The CDC’s National Vital Statistics Report highlights this worrying trend, showing a clear divide between the South and other regions.
Dietary habits and higher obesity rates also play significant roles (via Seattle Times). Understanding these challenges is crucial in addressing the health disparities that haunt the South.
Missouri’s Unexpected Placement

Missouri, a state not typically associated with the South, finds itself among the states with the lowest life expectancy, averaging 76.6 years. Urban-rural disparities, coupled with economic challenges, significantly impact Missourians’ health outcomes (via the Missouri Department of Health & Senior Services).
Unlike its Southern counterparts, Missouri’s unique positioning brings different health challenges, emphasizing the need for tailored public health interventions to combat its distinct issues.
The Challenges of West Virginia

West Virginia stands out for the wrong reasons, with the lowest life expectancy in the nation at 74.4 years. The state struggles with high rates of drug overdoses, obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
“It seems that the worst outcomes happen here first,” says Dr. Michael Brumage, a public health expert at West Virginia University, highlighting the dire health crisis facing the state (via The Associated Press). This situation demands urgent attention to reverse the troubling trends.
The Northeastern Edge

Contrastingly, the Northeast tells a different story, with states like New York and Massachusetts showcasing some of the highest life expectancies in the country (via Kent State Online).
These states benefit from robust health care systems, numerous exercise opportunities, and urban planning that promotes healthy living. The CDC’s findings illustrate how these factors contribute to longer lives and offer lessons for other regions grappling with health challenges.
California’s Longevity Leap

California has made impressive strides, jumping from 20th to second in longevity rankings since 1980. This leap is attributed to significant lifestyle changes among its residents, including reduced smoking rates and increased physical activity.
“Residents of California have significantly improved their lifestyle,” reports a 2019 USA Today article, highlighting the state’s journey toward healthier living.
The Coastal Connection
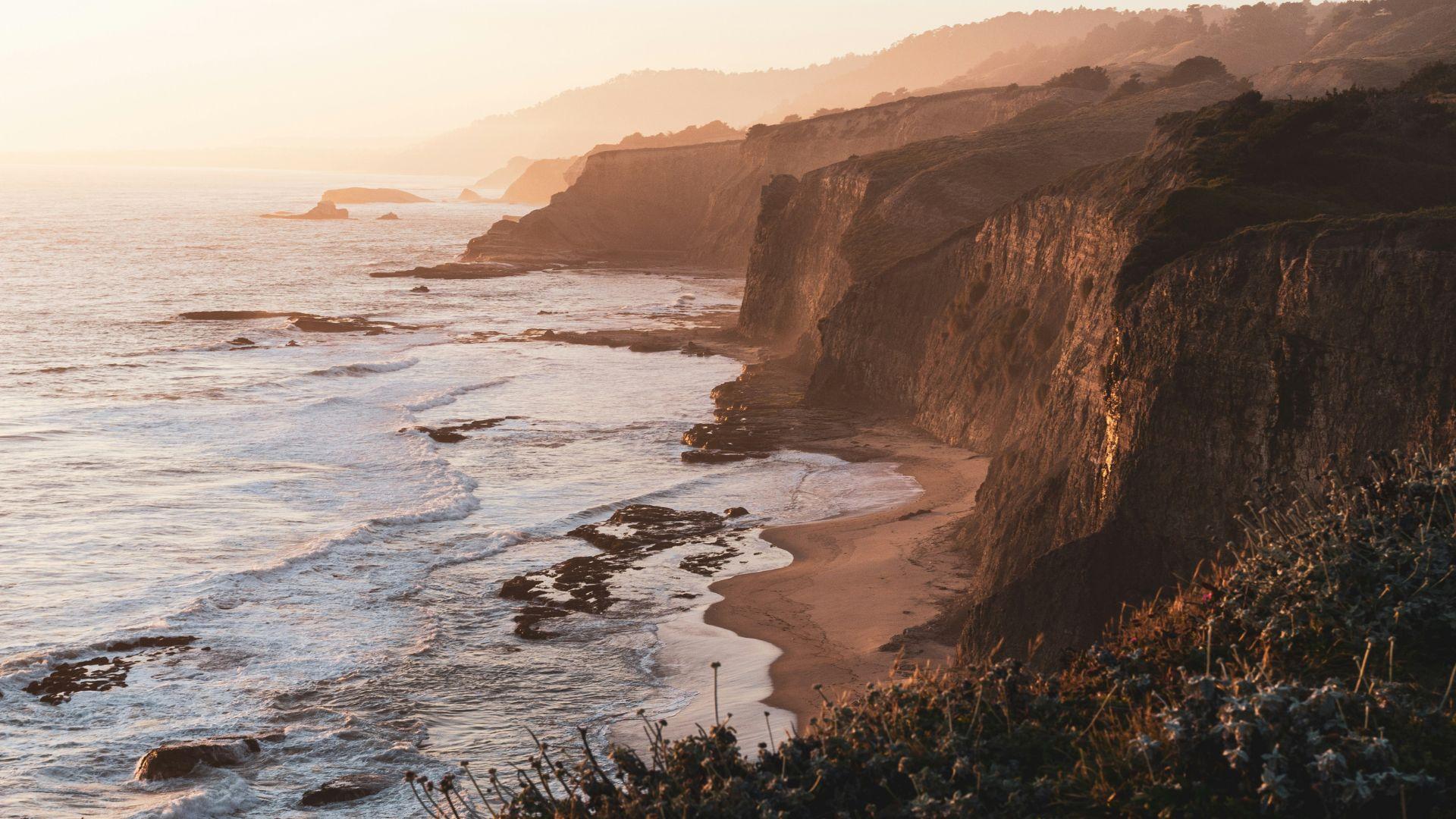

Living by the coast seems to offer more than just beautiful views and relaxing vibes. Coastal states like Rhode Island and Connecticut boast higher life expectancies, attributed to factors like better air quality and more opportunities for outdoor activities (via CNBC).
Dr. Lewis Elliott, an environmental psychologist, suggests that the coastal environment contributes to better mental and overall health, highlighting the benefits of seaside living (via Blue Health).
Florida’s Exception in the South
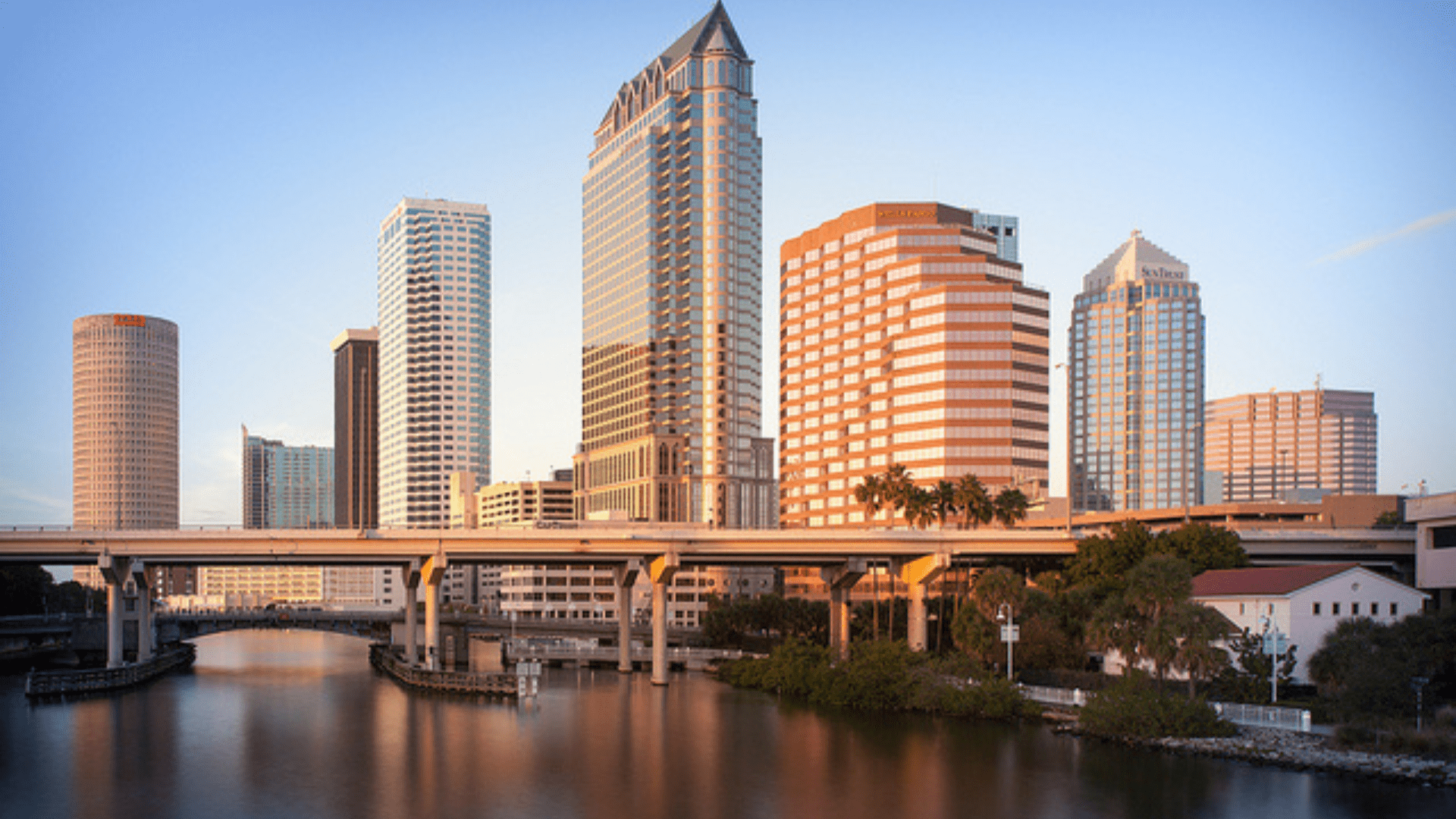

Florida stands as an anomaly in the South, with a higher average life expectancy of 78.9 years. The state’s large retiree population, focus on exercise, and improved health care accessibility defy the typical Southern trend.
Florida’s example shows that with the right policies and health initiatives, states can overcome regional health disparities and improve their residents’ longevity, particularly those with an older median age, such as Florida (via Visual Capitalist).
Wyoming’s Silent Crisis
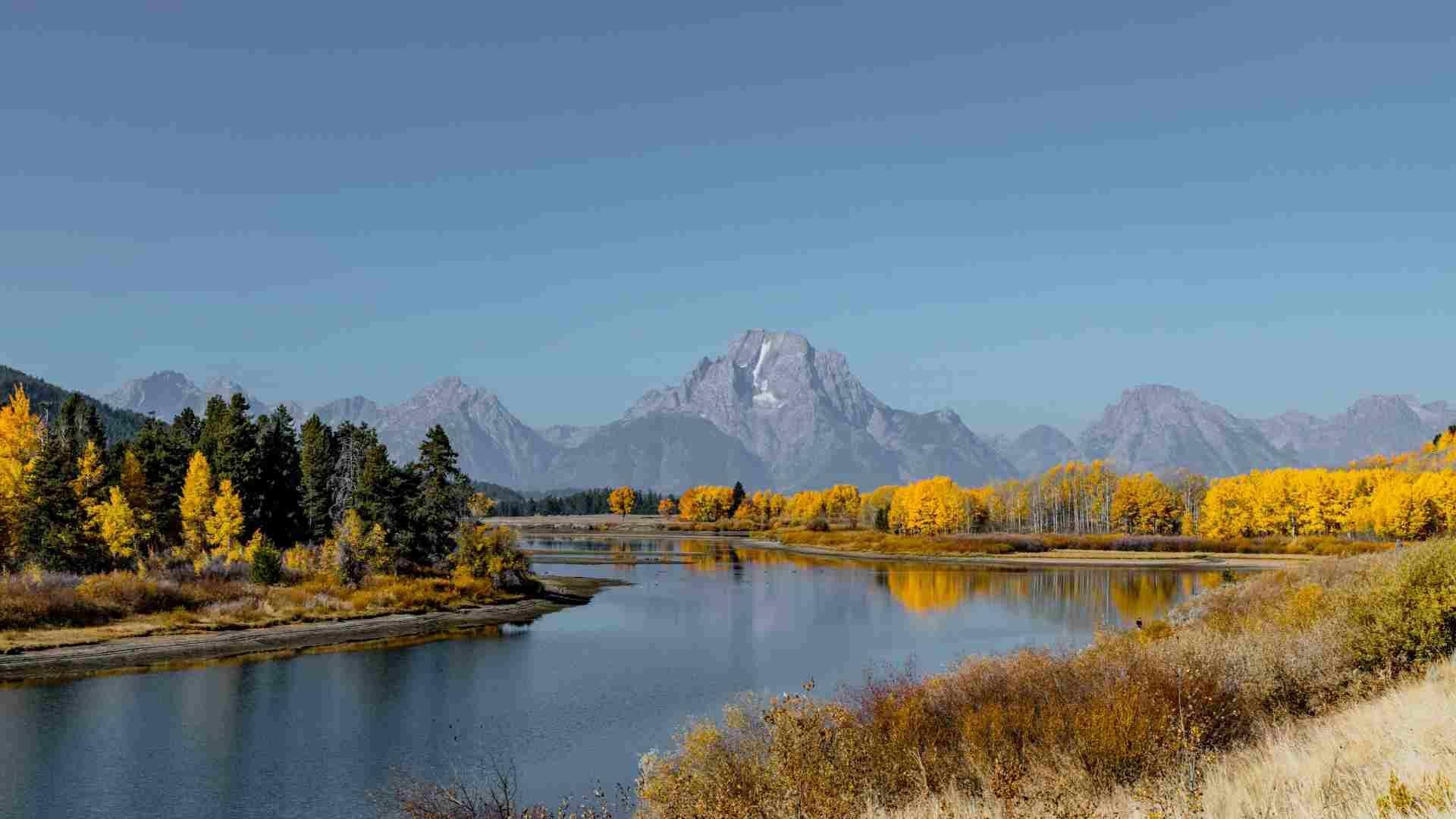

Wyoming’s struggle with high suicide rates and the impacts of gun ownership illustrates another aspect of health affecting longevity. The state’s suicide rate, one of the highest in the nation, points to underlying mental health and policy issues that need urgent attention (via NPR).
Addressing these concerns is crucial for improving the overall well-being and life span of Wyoming’s residents.
Alaska’s Unique Health Risks
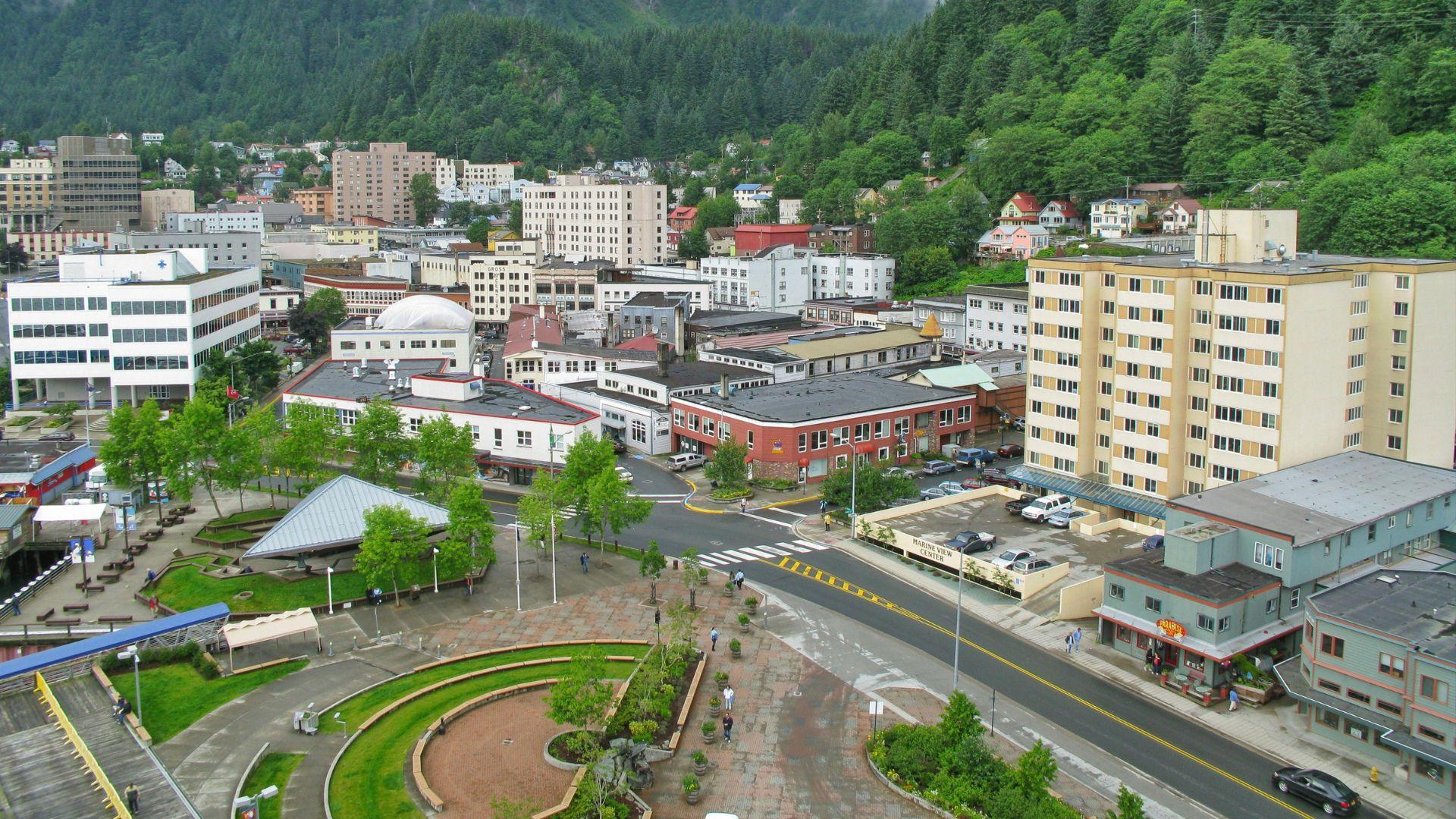

Alaska’s life expectancy paints a complex picture, with unique challenges such as high occupational fatalities and environmental hazards affecting its residents’ longevity. Despite its natural beauty, the state faces issues like a high rate of hypothermia deaths and violent crime (via Alaska Public Media).
Understanding these unique conditions is key to addressing the health and safety concerns that are lowering Alaskans’ life expectancy.
New York’s Diverse Life Expectancy

New York exemplifies the stark disparities within a single state, where life expectancy can significantly differ from one neighborhood to another. Economic disparities play a huge role, as seen in the gap between residents of affluent Manhattan areas and those in the South Bronx or Brownsville (via City Limits).
This disparity highlights the broader issue of socioeconomic status as a determinant of health and longevity.
Bridging the Longevity Gap
The disparities in life expectancy across the United States serve as a call to action. By understanding and addressing the unique challenges faced by different states, we can work toward bridging the health divide.
Learning from the successes of states like California and Florida can guide other regions in improving their public health strategies. Ultimately, a concerted effort across all levels of society is required to ensure that all Americans can enjoy a longer, healthier life.








































